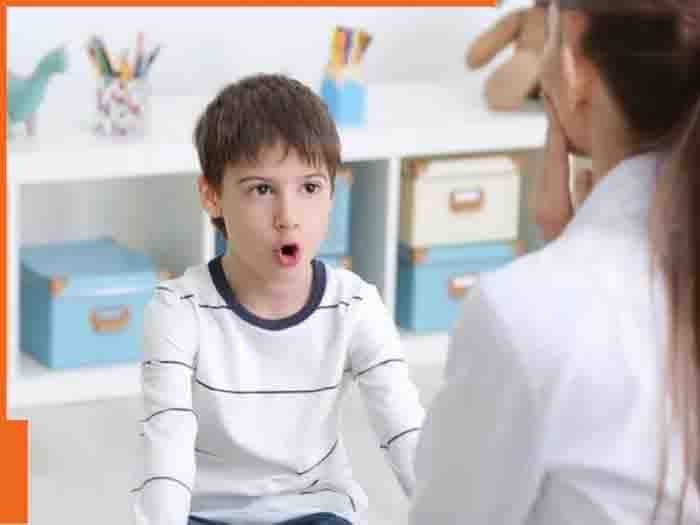
Stammering Symptoms: Stuttering is also called stammering or stuttering. This is a neurological condition. In this, the child talks haltingly. In this condition, one starts feeling difficulty in speaking words and sentences easily. The problem related to this starts between the ages of 3 to 5 years. If it is not treated in time, this problem can persist for a long time. In such a situation, it is very important to know about it.
Types of stuttering
Development Stammering
This is the most common type of stuttering, the symptoms of which usually appear in childhood. In the case of developmental stammering, one starts having trouble speaking words clearly.
Acquired Stammering
This is called late stammering. It includes neurogenic stammering and psychogenic stammering.
1. Neurogenic stammering
Neurogenic stammering can occur due to damage to the central nervous system. This can also increase the risk of stroke.
2. Psychogenic stammering
Cases of psychogenic stammering usually develop after an emotional trauma.
Symptoms of Stuttering
- Trembling lips or rapid blinking of eyes while speaking
- feeling hesitant or afraid
- repeating words, phrases, or sentences
- Drawing the first letters of words
- feeling stuck or obstructed
- Excessive use of filler words like umm or ah
- try to avoid speaking
- Stuttering when anxious, stressed, or tired
Causes of stuttering
The causes of stuttering are not fully understood, but it is believed to be a combination of genetic disorders, brain development, and environmental factors.
Risk Factors
- Genetic Disorders
- try to speak quickly
- stress or anxiety
- Tiredness
- Illness or injury
Preventive measures
- Encourage the child to speak slowly and clearly.
- Do not pressure the child to talk.
- Talk to the child in a calm and comfortable environment.
- Listen to the child carefully and do not interrupt him.
- Praise the child's positive qualities.
- Speak slowly and deliberately.
- Do breathing exercises.
- Doing speech practice.
- Reducing anxiety and stress.
--Advertisement--

 Share
Share